Xpansiv





Press

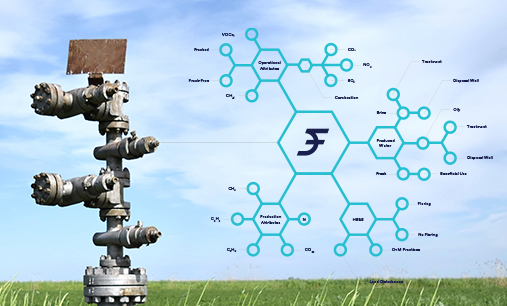
“Natural gas is recognized as a relatively clean transition fuel, but methane losses due to leaks, venting, and uncontrolled flaring negate its climate advantages,” said Jeff Cohen, Xpansiv co-founder and Sustainability Director. “The data exist, but until now markets have not provided incentives to reward responsibly produced natural gas. Xpansiv is unlocking the value in current production with verified, empirical data that authenticates and registers operations with low methane emissions; we’re differentiating a commodity that’s been traditionally undifferentiated.”
“Until now, the gas being consumed by a utility or industrial user was impossible to trace,” Cohen said. “What MPCs allow is for an end-user to invest in and support the production of responsibly produced natural gas, with auditable data back to the specific facility and time it was extracted.”

The exchange-traded market has contributed to the development of derivatives markets in other nascent markets, including by enabling firms to hedge using exchange contracts. ISDA supports the continued development of standardized contracts by exchanges, such as the N-GEO and GEO futures contracts jointly developed by Xpansiv and CME Group in 2021.

A senior employee at CME Group has taken on a carbon markets role at Xpansiv… Russel Karas has been appointed Head of Carbon Market Development on Xpansiv’s International Carbon Team, working on expanding the company’s portfolio of standardised voluntary emissions reduction (VER) contracts.
Karas is the second veteran CME employee to move to Xpansiv in as many months, with carbon markets veteran Henrik Hasselknippe in October becoming the ESG firm’s Head of Markets and Head of European Operations.

Energy and commodities markets information, benchmark and analytics provider S&P Global Platts and ESG-focused commodities marketplace provider Xpansiv announced today the launch of a new partnership aimed at advancing transparency in the global carbon markets space. Under the new collaboration, the companies will work together on the development and distribution of assessed daily closing prices for voluntary carbon market (VCM) instruments.
Saugata Saha, President, S&P Global Platts, said: “The voluntary markets have the potential to play a pivotal role in helping close the gap between what governments can deliver and what the world needs to achieve in terms of overall emissions reductions. The value of the market is now more than $1 billion and forecast to increase fifteen-fold by 2030, according to the Taskforce on Scaling Voluntary Carbon Markets. Our suite of VCM assessments is providing increased transparency and understanding of these markets, and this partnership with Xpansiv will enable us to develop scalable opportunities as this market continues to evolve.”

Demand for offsets is soaring. More credits were traded in the first eight months of this year than in all of 2020, according to BloombergNEF, as companies and governments spend billions of dollars to meet net-zero emissions targets and burnish their green credentials.
In the coming years, the UN credits could become a kind of global benchmark, with other voluntary carbon credit prices trading in relation, according to Henrik Hasselknippe, who’s in charge of carbon exchanges at Xpansiv, where more than 100 million metric tons of the credits have traded this year.
“Markets can handle multiple standards,” Hasselknippe said. “That’s something that we see in many markets.”

A consortium led by Context Labs, the UNFCCC Climate Champions, and Xpansiv today announced the launch of the Commodity Genome Project™ (CGP), an open-source language for commodity markets housed at One Earth, a not-for-profit organization working to accelerate climate action. The CGP establishes a language for describing commodities’ environmental, social, and governance (ESG) footprints—in addition to their physical attributes. The project’s goal is to accelerate the proliferation of sustainable commodity standards by 2030 by creating a common language for describing the comprehensive data profile for any given unit of commodity production. This collective framework
will serve as an essential foundation upon which new standards can be built.
By enabling clear comparisons of ESG footprints and ensuring the integrity of product information, the CGP empowers markets to appropriately value the materials at the base of global supply chains. This paradigm shift in commodity valuation can potentially redirect trillions of dollars toward regenerative production practices. The CGP was created as a public good, and participants are collaborating to define new digital ESG-inclusive commodities and price signals.






